September 2, 2025
Mathematics education in the District of Columbia Public Schools (DCPS) is an engaging, dynamic student-centered learning experience. Guided by teachers’ deep knowledge of the Common Core Content and Practice Standards, students will be motivated and challenged as they develop conceptual understanding, apply understanding to unfamiliar, real world mathematical situations, and fluently manipulate numbers and symbols. Through these engaging experiences, students will develop competency in the eight mathematical practices. Teachers and students have access to high-quality Common Core-aligned curricular resources, purposeful and actionable data obtained from quality assessments, and targeted professional development designed to support teachers and staff in the implementation of the DCPS Mathematics Instructional Block.
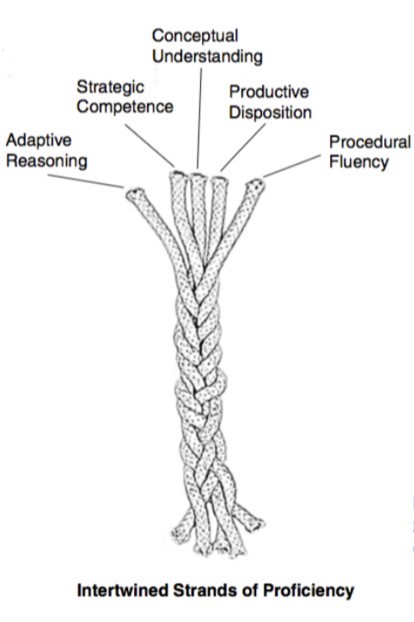
DCPS math instruction is designed around the research and best practice in mathematics education, namely in helping students develop the 5 strands of mathematical proficiency. For more information about the 5 strands of proficiency, visit this site.
In K-5, DCPS utilizes the Eureka Math Squared curriculum. For middle and high school, DCPS uses Illustrative Mathematics. For more information on the units of study by grade level, see below.
Major Units of Study
| Elementary School Units by Grade Level | |||||
|
Kindergarten |
Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | Grade 5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Middle School Units by Grade Level | ||
| Grade 6 | Grade 7 | Grade 8 |
|
|
|
| High School Units | ||
| Algebra I | Geometry | Algebra 2 |
|
|
|
Contact Information
Rhonda Idris, Director, STEM Strategy
Jessica Gonzalez, Director, Secondary Math
Kaila Ramsey Garza, Director, Elementary Math & Science